Are L Carnitine and L Carnosine the Same?
 There are many types of supplements, and knowing which one to choose can be challenging. That’s why it’s essential to understand the differences between them. You can usually tell by the name, but sometimes even that isn’t enough.
There are many types of supplements, and knowing which one to choose can be challenging. That’s why it’s essential to understand the differences between them. You can usually tell by the name, but sometimes even that isn’t enough.
Take L-carnitine and L-carnosine, for instance: on the surface, they sound very similar – but when you look closely, some critical differences make them stand apart.
In this article, we’ll explore those differences so you can decide which one is right for you.
What is L-Carnitine?
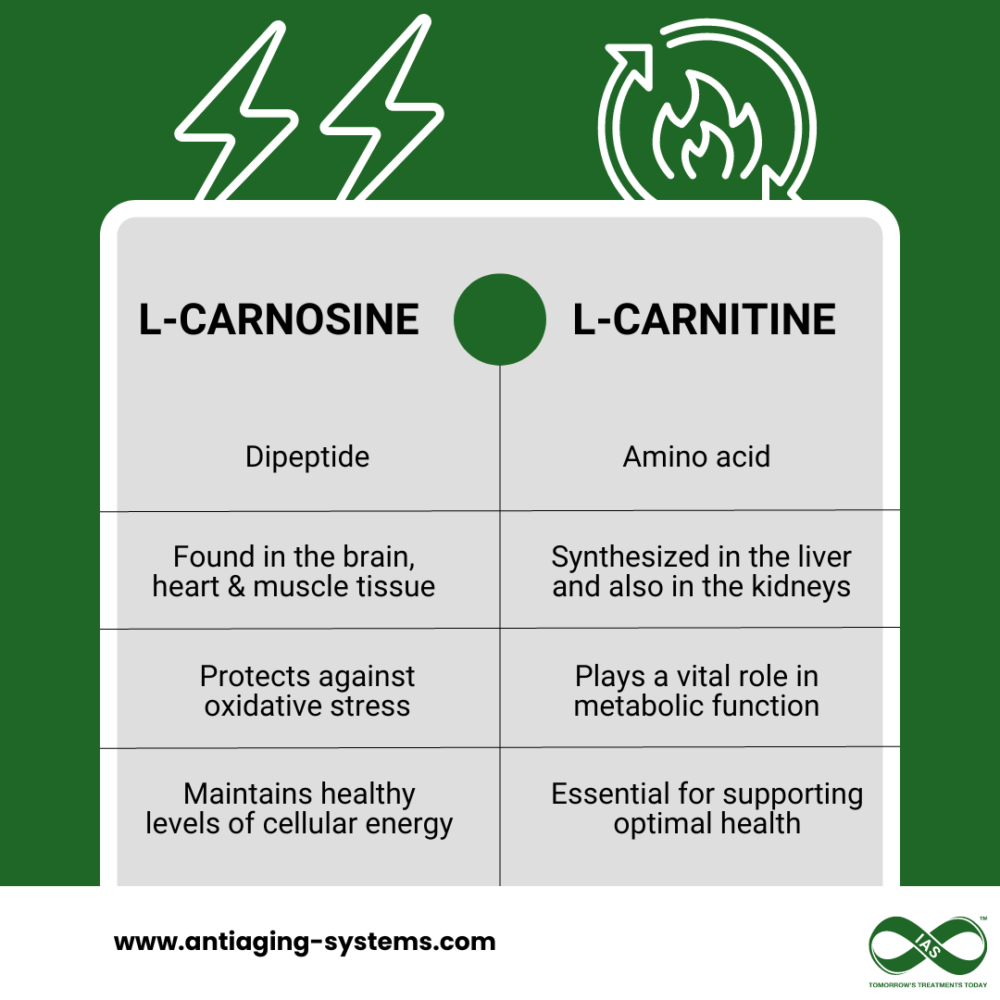
L-carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid that helps your body generate energy from fat. It plays a vital role in metabolism, helping to transport long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria (our cell’s powerhouse), where they are used for energy production [1].
Mitochondrial function is essential for optimal health, and research suggests that supplementing with L-carnitine could potentially help support it [2]. Healthy L-carnitine levels are also associated with improved weight management, exercise performance, and healthy aging.
You can get L-carnitine from animal products such as meat, fish, and dairy or take it in supplement form.
Our bodies can also produce L-carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine, but some people may benefit from taking an additional supplement to ensure they’re getting enough [3].
What is L-Carnosine?
On the other hand, L-carnosine is a naturally occurring dipeptide made up of two amino acids: alanine and histidine. Found naturally in muscle tissue, the brain, and the heart, L-carnosine is a protein-building block that helps maintain cellular health and support the body’s antioxidant defenses [4].
L-carnosine works in different ways than L-carnitine. It helps to protect against oxidative damage and fight the aging process, helping to maintain healthy levels of cellular energy. It’s also been studied for its potential in preventing and treating age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s Disease [5].
While our bodies can create L-carnosine, it’s also found in beef, pork, and chicken. You can also get it from certain supplements if you’re looking to increase your intake.
The Differences Between L-Carnitine and L-Carnosine
The main difference between L-carnitine and L-carnosine is that L-carnitine helps to convert fat into energy. Whereas, L-carnosine works to preserve cellular health and maintain many normal bodily functions.
They are also made up of different amino acids: L-carnitine is composed of lysine and methionine, while L-carnosine is composed of alanine and histidine.
Aside from their composition and function, they also offer different bodily benefits. Let’s take a look at some of the potential benefits of each:
Benefits of L-Carnitine
- May aid in weight loss as it moves fatty acids to cells to be burned as energy
- Improve energy levels by helping to manage and transport fats
- Can help prevent age-related mental decline and improve brain function [6]
- Can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood sugar levels for those with Type 2 Diabetes
- It may improve heart function and reduce diastolic blood pressure [7]
- Can help with nerve regeneration, which may aid those with nerve damage
Benefits of L-Carnosine
- May protect against oxidative damage and slow the aging process
- Can help prevent age-related mental decline and improve brain function [8]
- Can counteract the harmful effects of sugar binding to proteins (glycation) which is linked to diseases like Alzheimer’s and other age-related conditions [9]
- Can improve exercise performance in athletes
- Provides support for healthy kidney and liver function
While both L-carnitine and L-carnosine may provide many benefits, you should always seek medical advice if you or a loved one have any health concerns.
Are There Any Noted Similarities Between L-Carnitine and L-Carnosine?
While they have different functions, both L-carnitine and L-carnosine are naturally occurring compounds found in the human body. They can both be obtained from food sources and offer potential health benefits.
They are also referred to as amino acids because they are both made up of two amino acids, though they do not share the same composition.
However, the similarities do not outweigh the significant differences between L-carnitine and L-carnosine. It’s important not to mix them up as they impact the body differently.
Conclusion
Though they may sound similar, you need to be aware of some important differences between L-carnitine and L-carnosine. Depending on your health goals, one or the other may be better suited to your individual needs.
Remember, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns about your health.
Links to related products
- LacticPro™ – High dose Carnosine to help energy production and inhibit the build up of lactic acid in the muscles and tissues.
- EnergyPro™ – contains Acetyl –L-Carnitine (ALCAR) which transports fatty acids to mitochondria, which turn them into ATP to increase energy production.
- ATP – A mitochondrial energy enhancer which acts a natural way to boost energy stores.
References:
[3] Carnitine Deficiency – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)


